Have you ever wondered how these colossal structures, hydroelectric dams, harness the power of flowing water to light up our homes and power our industries? It's a fascinating process involving clever engineering and a deep understanding of physics. Let's dive into the heart of these energy giants and explore the science behind them.
Many people might think of dams as just concrete walls holding back water. Some might be concerned about the environmental impact of these structures. Perhaps they're curious about the specific engineering feats that make hydroelectricity possible, or maybe they're simply seeking a clear explanation of how it all works together.
This blog post aims to demystify the inner workings of a hydroelectric dam. We'll explore the journey of water from reservoir to turbine, unraveling the engineering principles that transform potential energy into clean, renewable electricity. We'll also touch upon some of the history, design considerations, and interesting facts about these powerful structures.
We've explored how a hydroelectric dam leverages the force of gravity and the potential energy of water to generate electricity. From the intake to the turbine, the generator to the power lines, each component plays a vital role in this process. We’ve also touched upon important aspects like dam types, environmental considerations, and the ongoing evolution of hydroelectric technology.
My First Encounter with Hydroelectric Power
The goal of this section is to share a personal anecdote that illustrates the power and impact of hydroelectric energy, connecting it to the reader on a more relatable level and then delving deeper into the specifics of how hydroelectric dams function. I remember visiting the Hoover Dam as a child. I was absolutely awestruck by its sheer size and the immense lake it created. Our tour guide explained how the dam generated electricity for millions of people, and I was completely captivated by the idea of turning something as simple as water into power. At that young age, the concept of potential energy and kinetic energy was beyond me, but the tangible result – the bright lights of Las Vegas powered by this massive structure – made a lasting impression. That experience ignited a lifelong curiosity about engineering and renewable energy sources.
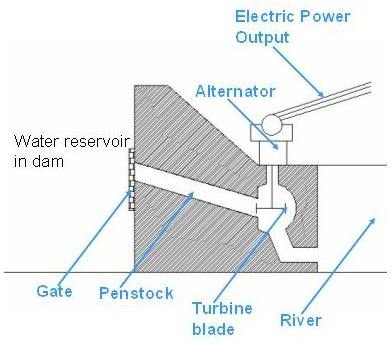
Hydroelectric dams work by converting the potential energy of stored water into kinetic energy, which then drives turbines connected to generators. The height of the water behind the dam, known as the head, is a critical factor in determining the amount of energy that can be generated. The higher the head, the greater the potential energy, and the more powerful the electricity generation. When water is released from the reservoir, it flows through a penstock, a large pipe that channels the water towards the turbine. The force of the water spins the turbine blades, which are connected to a generator. The generator uses electromagnetic induction to convert the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy. This electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses.
The Anatomy of a Hydroelectric Dam
This section aims to break down the different components of a hydroelectric dam, explaining their functions and how they contribute to the overall process of electricity generation. Dams have existed for centuries, primarily for irrigation and flood control. Early dams were simple structures made of earth or stone. The Romans were particularly skilled at building dams, and their aqueducts and reservoirs are testaments to their engineering prowess. However, the use of dams for electricity generation is a relatively recent development. The first hydroelectric power plant was built in 1882 in Appleton, Wisconsin. This small plant used a waterwheel to power a generator that lit two paper mills and a home.
The development of the modern hydroelectric dam is closely linked to the Industrial Revolution and the growing demand for electricity. As technology advanced, engineers were able to design larger and more efficient dams that could generate vast amounts of power. The Hoover Dam, completed in 1936, was a landmark achievement in engineering and a symbol of American ingenuity. Its construction required massive amounts of concrete and steel, and it created Lake Mead, one of the largest reservoirs in the world. Today, hydroelectric dams are a significant source of renewable energy worldwide.
Hidden Secrets of Dam Design
This section will delve into the less obvious aspects of dam design and construction, highlighting the challenges engineers face and the innovative solutions they employ to ensure safety and efficiency. The success of a hydroelectric dam hinges on its ability to withstand immense pressure from the water it impounds. The design must account for factors such as the geological composition of the site, the potential for earthquakes, and the risk of flooding. Engineers use sophisticated computer models to simulate the stresses on the dam and ensure that it can withstand extreme conditions. Dams are also equipped with spillways, which are channels that allow excess water to be released in a controlled manner. Spillways prevent the dam from being overtopped during periods of heavy rainfall or snowmelt, which could lead to catastrophic failure. Furthermore, dams are constantly monitored for signs of stress or damage. Sensors embedded in the concrete measure temperature, pressure, and movement.
This data is analyzed by engineers to identify potential problems and take corrective action before they escalate. Another hidden secret of dam design is the importance of fish passage. Dams can block the migration of fish, disrupting their life cycles and harming fish populations. To mitigate this impact, many dams are equipped with fish ladders, which are series of steps that allow fish to swim upstream past the dam. Fish screens are also used to prevent fish from being drawn into the turbines. These measures help to ensure that hydroelectric dams can coexist with healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Choosing the Right Dam Type
This section will offer guidance on the different types of hydroelectric dams and the factors that determine which type is best suited for a particular location. Not all dams are created equal. Different types of dams are designed to suit different terrains and geological conditions. The most common types of dams are gravity dams, arch dams, and embankment dams. Gravity dams are massive structures that rely on their weight to resist the force of the water. They are typically built in wide, relatively flat valleys where there is a solid rock foundation. Arch dams are thinner and more curved than gravity dams, and they transfer the force of the water to the abutments, which are the walls of the valley. Arch dams are well-suited for narrow, steep-sided canyons where there is strong rock on both sides of the valley.
Embankment dams are made of earth or rockfill, and they rely on their shape and internal structure to resist the force of the water. Embankment dams are less expensive to build than gravity dams or arch dams, but they require a wider valley and a stable foundation. The choice of dam type depends on a variety of factors, including the topography of the site, the geological conditions, the availability of materials, and the cost of construction. Engineers carefully analyze these factors to determine which type of dam is the most appropriate for a particular project.
The Environmental Impact of Hydroelectric Dams
Hydroelectric dams, while a source of renewable energy, can have significant environmental impacts. This section will discuss these impacts and the measures that can be taken to mitigate them. The creation of a reservoir behind a dam can flood large areas of land, displacing communities and destroying habitats. The altered flow regime downstream of the dam can also affect aquatic ecosystems, impacting fish populations and other wildlife. Dams can also trap sediment, which can reduce the fertility of downstream agricultural lands. To mitigate these impacts, engineers are increasingly incorporating environmental considerations into dam design and operation.
Fish ladders and fish screens, as mentioned earlier, are used to protect fish populations. Environmental flow releases are also implemented to mimic natural flow patterns and maintain healthy aquatic ecosystems. In some cases, dams are even removed to restore rivers to their natural state. The decision to build a hydroelectric dam requires careful consideration of the environmental impacts and the potential benefits. It is essential to strike a balance between the need for renewable energy and the preservation of natural ecosystems. Furthermore, the long-term sustainability of hydroelectric dams depends on proper maintenance and management.
Tips for Visiting a Hydroelectric Dam
If you're planning a trip to a hydroelectric dam, this section will offer practical advice on how to make the most of your visit, including what to expect, what to wear, and what to look for. Visiting a hydroelectric dam can be an educational and awe-inspiring experience. Before you go, it's a good idea to do some research on the dam's history, engineering, and environmental impact. This will give you a better appreciation for the scale and complexity of the project. When you arrive, be sure to take a guided tour if one is available. The tour guides are often knowledgeable engineers or historians who can provide valuable insights into the dam's design and operation.
As for what to wear, comfortable shoes are a must, as you'll likely be doing a lot of walking. You should also bring a jacket or sweater, as the temperature inside the dam can be cooler than outside. And don't forget your camera! Hydroelectric dams are impressive structures, and you'll want to capture the experience. During your visit, pay attention to the different components of the dam, such as the intake, the penstock, the turbine, and the generator. Try to visualize how the water flows through the dam and how it generates electricity. Also, take some time to reflect on the environmental impact of the dam and the measures that are being taken to mitigate it.
The Future of Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power has been a cornerstone of renewable energy for over a century, but what does the future hold? This section will explore the trends and innovations that are shaping the future of hydroelectric technology. The development of new materials and technologies is enabling engineers to design more efficient and sustainable hydroelectric dams. Advanced turbines are capable of generating more electricity with less water, and new dam designs are minimizing the environmental impact. Pumped storage hydroelectricity is also gaining popularity as a way to store excess energy from other renewable sources, such as solar and wind.
Pumped storage involves pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir during periods of low demand, and then releasing the water back down to generate electricity during periods of high demand. This technology can help to stabilize the grid and ensure a reliable supply of renewable energy. Another promising trend is the development of small-scale hydroelectric projects. These projects can be built on smaller rivers and streams, providing a source of clean energy for remote communities. Small-scale hydroelectric projects can also be less environmentally damaging than large-scale dams. As the world transitions to a cleaner energy future, hydroelectric power will continue to play a vital role.
Fun Facts About Hydroelectric Dams
This section will share some interesting and surprising facts about hydroelectric dams, adding a touch of fun and intrigue to the discussion. Did you know that the Three Gorges Dam in China is the largest hydroelectric dam in the world? It has a generating capacity of 22,500 megawatts, which is enough to power millions of homes. Or that the Hoover Dam was built during the Great Depression, providing jobs for thousands of unemployed workers? The construction of the Hoover Dam was a monumental feat of engineering, and it is a testament to the ingenuity and perseverance of the American people.
Here's another fun fact: some hydroelectric dams are designed to be reversible, meaning that they can pump water uphill to store energy and then release it back down to generate electricity. These dams are known as pumped storage hydroelectric facilities, and they are a valuable tool for managing the variability of renewable energy sources. And finally, did you know that some hydroelectric dams are built underground? These underground dams are less visible and have a smaller environmental impact than traditional dams.
How to Advocate for Responsible Hydroelectric Development
This section will provide practical advice on how individuals can support responsible hydroelectric development, ensuring that it is done in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner. One of the best ways to advocate for responsible hydroelectric development is to stay informed about the issues. Read news articles, research government policies, and attend public forums to learn more about the potential impacts of hydroelectric projects. Another way to make a difference is to support organizations that are working to promote sustainable energy development. These organizations can provide you with resources and opportunities to get involved in advocacy efforts.
You can also contact your elected officials and let them know that you support responsible hydroelectric development. Encourage them to support policies that promote renewable energy and protect the environment. Finally, consider making personal choices that reduce your energy consumption. By using less electricity, you can reduce the demand for new energy projects, including hydroelectric dams. Simple steps like turning off lights when you leave a room, using energy-efficient appliances, and conserving water can make a big difference.
What If Hydroelectric Dams Didn't Exist?
This section will explore the potential consequences of a world without hydroelectric dams, highlighting the vital role they play in providing clean, renewable energy. Without hydroelectric dams, the world would be much more reliant on fossil fuels for electricity generation. This would lead to increased greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. The absence of hydroelectric dams would also reduce the availability of renewable energy, making it more difficult to meet global climate goals.
In addition to providing electricity, hydroelectric dams also provide other benefits, such as flood control and water supply. Without dams, communities would be more vulnerable to flooding, and water shortages would be more common. The absence of hydroelectric dams would also impact agriculture, as many irrigation systems rely on water stored in reservoirs behind dams. While hydroelectric dams have environmental impacts, they also provide significant benefits to society. The challenge is to develop and operate hydroelectric dams in a responsible and sustainable manner.
5 Key Benefits of Hydroelectric Dams
This listicle will highlight five key advantages of hydroelectric dams, summarizing the main arguments in favor of this renewable energy source.
- Renewable Energy: Hydroelectric dams generate electricity from a renewable source of energy – water. This reduces our reliance on fossil fuels and helps to mitigate climate change.
- Clean Energy: Hydroelectric dams produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or air pollutants. This makes them a cleaner energy source than fossil fuel power plants.
- Flood Control: Hydroelectric dams can help to control flooding by storing water in reservoirs and releasing it in a controlled manner. This can protect communities and infrastructure from damage.
- Water Supply: Hydroelectric dams can provide a reliable source of water for irrigation, drinking water, and industrial uses. This is especially important in arid and semi-arid regions.
- Recreation: Reservoirs behind hydroelectric dams can provide opportunities for recreation, such as boating, fishing, and swimming. This can boost local economies and improve the quality of life for residents.
These are just a few of the many benefits of hydroelectric dams. While it's important to acknowledge the environmental drawbacks, and continue to improve to mitigate them, hydroelectric power remains a valuable source of clean, renewable energy.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about hydroelectric dams:
Q: How long do hydroelectric dams last?
A: With proper maintenance, hydroelectric dams can last for 50 to 100 years, or even longer. Regular inspections and repairs are essential to ensure the dam's structural integrity and prevent potential failures.
Q: What happens when a hydroelectric dam is decommissioned?
A: Decommissioning a hydroelectric dam is a complex process that involves removing the dam structure and restoring the river to its natural state. This can have significant environmental and economic impacts, and it requires careful planning and execution.
Q: Are there any new types of hydroelectric technology being developed?
A: Yes, there are several new types of hydroelectric technology being developed, including run-of-river hydroelectric projects, which have a smaller environmental impact than traditional dams, and pumped storage hydroelectric projects, which can store energy and help to stabilize the grid.
Q: How can I learn more about hydroelectric power?
A: There are many resources available online and in libraries that can provide you with more information about hydroelectric power. You can also visit a hydroelectric dam and take a guided tour to learn more about how it works.
Conclusion of How a Hydroelectric Dam Works: Inside the Engineering
Hydroelectric dams represent a remarkable feat of engineering, harnessing the power of water to provide clean and renewable electricity. While these structures present environmental challenges, ongoing advancements and a commitment to responsible practices can help to minimize their impact. By understanding the inner workings of these powerful systems, we can better appreciate their role in shaping our energy future.