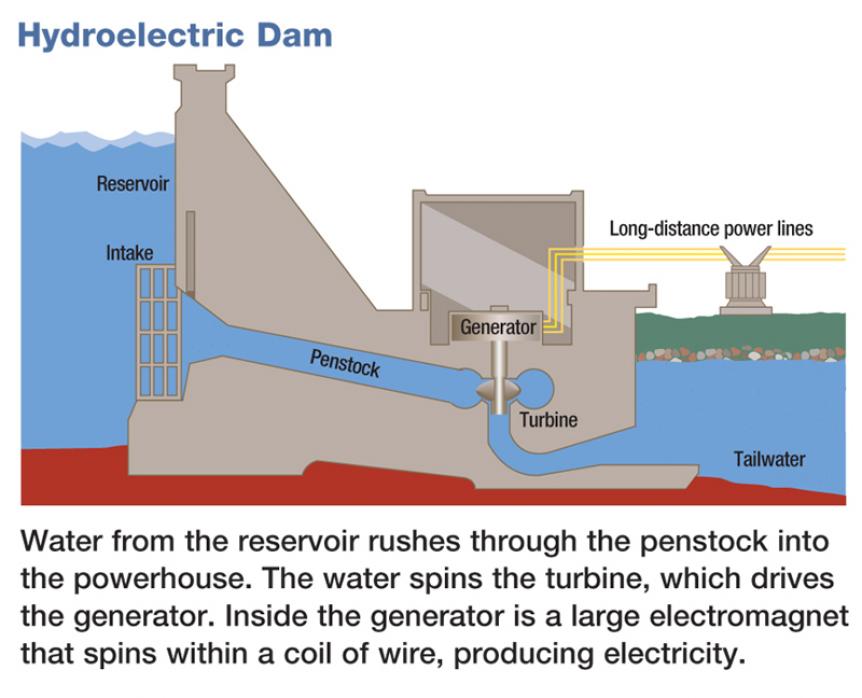
Imagine harnessing the raw, untamed power of a river, transforming its relentless flow into the electricity that lights our homes and powers our cities. Hydroelectric power, a concept as old as the waterwheel itself, offers a captivating blend of natural forces and human ingenuity. But how do we truly grasp its intricacies, and more importantly, how can we effectively explain it to others, especially students?
For both educators and learners, navigating the world of hydroelectric power can feel like navigating a complex maze. Jargon can be dense, the science can seem intimidating, and finding reliable, engaging resources can be a challenge. It's easy to get bogged down in technical details, losing sight of the bigger picture and the fundamental principles at play.
This post aims to illuminate the world of hydroelectric power for both students and teachers. We'll break down the core concepts in an accessible way, explore its history and impact, and offer practical tips for understanding and explaining this vital source of renewable energy. Get ready to dive in and unlock the secrets of hydroelectric power!
In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the fundamentals of hydroelectric power, its historical significance, potential environmental impacts, and exciting future prospects. We will explore hydroelectricity, dams, turbines, generators, renewable energy, sustainable energy, environmental impact, and energy efficiency. Together, we can empower ourselves and others with the knowledge to appreciate and understand this fascinating technology.
My First Encounter with Hydroelectric Power
My first real encounter with hydroelectric power wasn't in a textbook or a classroom, but during a family trip to the Hoover Dam. I was probably ten years old, and the sheer scale of the dam was awe-inspiring. I remember standing at the base, looking up at this massive concrete structure holding back the immense power of the Colorado River. It was more than just a big wall; it was a testament to human engineering. Inside, the hum of the turbines and the knowledge that this giant machine was converting the river's flow into electricity sparked a fascination that has stayed with me ever since. Seeing the tangible impact – the lights of Las Vegas shimmering in the distance – made the concept of renewable energy incredibly real and exciting. This experience fuels my passion for making complex topics like hydroelectric power accessible and engaging for everyone. Now, understanding the principles behind how falling water turns into electricity is key. The water flows through a penstock (a pipe or channel) and then spins the blades of a turbine. This turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy. The amount of electricity generated depends on the volume of water flow and the height from which it falls (the "head"). High head hydro plants typically use dams to create large reservoirs and store water, releasing it as needed to meet electricity demand. This contrasts with "run-of-river" plants, which divert a portion of the river's flow without creating significant storage.
What is Hydroelectric Power?
At its core, hydroelectric power is a way of generating electricity by using the force of moving water. Think of it like a giant water wheel, but instead of grinding grain, it's spinning a turbine connected to a generator. This generator then converts the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy, which can be transmitted to homes, businesses, and industries. The basic principle relies on gravity. Water stored at a higher elevation has potential energy. When that water flows downhill, that potential energy is converted into kinetic energy (the energy of motion). This kinetic energy is then harnessed by the turbine. There are several types of hydroelectric power plants, but the most common involve a dam that creates a reservoir. This reservoir stores water and allows for controlled release, ensuring a consistent supply for electricity generation. Other types include pumped storage hydropower, which pumps water uphill to a reservoir during periods of low electricity demand and releases it to generate electricity during peak demand. Run-of-river plants utilize the natural flow of a river without significant storage, and tidal power plants harness the energy of ocean tides. Each type has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on factors such as geographical location, environmental impact, and cost.
A History of Hydroelectric Power
The history of hydroelectric power stretches back centuries, long before the modern power grids we know today. The earliest forms of hydropower involved waterwheels, used to grind grain, saw lumber, and power other mechanical tasks. Evidence of waterwheels dates back to ancient Greece and Rome. However, the modern era of hydroelectric power truly began in the late 19th century with the invention of the electric generator. In 1882, the first hydroelectric power plant was built in Appleton, Wisconsin, using the Fox River to power a paper mill and a few homes. This marked a pivotal moment, demonstrating the potential to generate electricity from water on a larger scale. The 20th century saw a boom in hydroelectric development, with massive dams and power plants built around the world. The Hoover Dam, completed in 1936, became an icon of American engineering and a symbol of the potential of hydroelectric power. While hydropower is a mature technology, innovation continues. Modern research focuses on improving turbine efficiency, minimizing environmental impacts, and developing new types of hydro plants, such as pumped storage and tidal power. The future of hydroelectric power will likely involve a mix of new projects and upgrades to existing facilities, with a focus on sustainability and environmental stewardship. There are some myths about the Hoover Dam, some claim that bodies are burried within it, but this has been debunked.
The Hidden Secrets of Hydroelectric Power
Beyond the basic mechanics of dams and turbines, lies a complex interplay of factors that determine the true potential and impact of hydroelectric power. One of the "hidden secrets" lies in understanding the delicate balance between power generation and environmental sustainability. While hydroelectricity is often touted as a clean and renewable energy source, it's crucial to acknowledge its potential environmental consequences. Dams can disrupt river ecosystems, altering water flow, blocking fish migration, and impacting water quality. However, modern dam designs and operational practices are increasingly focused on mitigating these impacts. Fish ladders and other fish passage technologies help fish migrate upstream and downstream, while minimum flow requirements ensure that rivers maintain sufficient water levels to support aquatic life. Another "secret" lies in optimizing plant efficiency. Even small improvements in turbine design and plant operation can lead to significant gains in power output. Advanced monitoring and control systems help operators optimize water flow and turbine speed to maximize electricity generation while minimizing water waste. Furthermore, the integration of hydroelectric power with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, is becoming increasingly important. Hydro plants can act as a flexible backup, providing power when solar and wind generation fluctuate. Pumped storage hydro can store excess energy from these sources and release it when needed, helping to stabilize the grid and ensure a reliable supply of renewable energy.
Recommendations for Understanding Hydroelectric Power
For students and teachers alike, a multifaceted approach is key to truly grasping hydroelectric power. Start with the fundamentals: clearly understand the basic principles of energy conversion, the different types of hydro plants, and the roles of turbines and generators. Visual aids are incredibly helpful. Diagrams, animations, and videos can bring these concepts to life and make them easier to understand. Consider visiting a hydroelectric power plant if possible. Seeing the scale of the operation and the inner workings of the machinery can be a powerful learning experience. Research real-world case studies. Explore the history and impact of different hydroelectric projects, both successful and controversial. This can help students understand the complexities and trade-offs involved in hydropower development. Engage in hands-on activities. Build a simple model of a hydroelectric power plant using everyday materials. This can help students visualize the process and reinforce their understanding of the underlying principles. Discuss the environmental and social impacts of hydroelectric power. Encourage critical thinking and debate about the benefits and drawbacks of this energy source. Finally, stay up-to-date on the latest developments in hydroelectric technology and research. The field is constantly evolving, with new innovations and approaches emerging all the time.
Delving Deeper: Environmental Impact Considerations
While hydroelectric power offers a clean alternative to fossil fuels, it's essential to understand its potential environmental consequences. Dams can significantly alter river ecosystems, impacting water flow, sediment transport, and fish populations. Changes in water temperature and oxygen levels can also affect aquatic life. Furthermore, the construction of dams can flood vast areas of land, displacing communities and destroying habitats. Greenhouse gas emissions from reservoirs can also be a concern, especially in tropical regions where decaying vegetation releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas. However, modern hydroelectric projects are increasingly designed with environmental mitigation measures in mind. Fish ladders and other fish passage technologies help fish migrate around dams, while minimum flow requirements ensure that rivers maintain sufficient water levels to support aquatic life. Selective water withdrawal systems can help regulate water temperature and oxygen levels, minimizing impacts on aquatic ecosystems. Furthermore, environmental impact assessments are conducted to evaluate the potential consequences of hydroelectric projects and identify ways to minimize harm. Sustainable hydropower development requires a careful balancing act between energy production and environmental protection. By considering the full range of environmental impacts and implementing appropriate mitigation measures, we can harness the benefits of hydroelectric power while minimizing its negative consequences. Hydropower is also known to increase methane emissions, which is important to understand in detail.
Tips for Explaining Hydroelectric Power
Explaining hydroelectric power effectively requires breaking down complex concepts into simpler, more digestible pieces. Start by focusing on the basic principles of energy conversion: potential energy of water stored at a height, kinetic energy of moving water, and the conversion of kinetic energy into electrical energy. Use relatable analogies. Compare the turbine to a water wheel or a bicycle dynamo to illustrate how mechanical energy is converted into electricity. Employ visual aids liberally. Diagrams, animations, and videos can be incredibly effective in conveying complex concepts. Avoid jargon as much as possible. Use clear, simple language that is appropriate for the audience. Encourage questions and discussion. Create a safe and supportive environment where students feel comfortable asking questions and sharing their ideas. Relate the topic to real-world examples. Discuss the role of hydroelectric power in providing electricity to homes, businesses, and communities. Highlight the benefits and drawbacks of hydroelectric power. Encourage critical thinking and debate about the pros and cons of this energy source. Emphasize the importance of sustainability. Discuss the environmental and social impacts of hydroelectric power and the need for responsible development. Tailor your explanation to the audience. Adjust your language and examples to suit the age and background of your students. Remember that teaching is not just about imparting information, it's about inspiring curiosity and fostering a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Engaging Students: Hands-On Activities
One of the best ways to engage students with hydroelectric power is through hands-on activities. Building a simple model of a hydroelectric power plant can be a fun and effective way to illustrate the basic principles. Use a plastic bottle, a small water wheel (or a homemade version), and a miniature generator (or a small DC motor) to create a working model. Students can experiment with different water flow rates and turbine designs to see how they affect electricity generation. Another engaging activity is to conduct a simple experiment to demonstrate the relationship between water height and potential energy. Fill a container with water and punch a small hole near the bottom. Measure the distance the water squirts out when the container is full compared to when it is half full. This will illustrate how the height of the water (the "head") affects the force of the water and its ability to do work. Furthermore, consider organizing a debate or role-playing activity where students take on different perspectives on hydroelectric power. Some students can represent environmental groups, while others can represent energy companies or local communities. This can help students understand the complexities and trade-offs involved in hydropower development and encourage critical thinking about its environmental and social impacts. By making learning interactive and engaging, you can help students develop a deeper understanding and appreciation for hydroelectric power.
Fun Facts About Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power boasts a wealth of fascinating facts that can spark curiosity and make learning more engaging. Did you know that the world's largest hydroelectric power plant, the Three Gorges Dam in China, has a generating capacity of over 22,500 megawatts? That's enough to power millions of homes! Or that some hydroelectric plants use pumped storage to essentially "store" energy by pumping water uphill to a reservoir during off-peak hours and releasing it to generate electricity during peak hours? Another interesting fact is that hydroelectric power is one of the oldest forms of electricity generation, with the first hydroelectric power plant built in the United States in 1882. Furthermore, the shape of a dam can influence its stability and efficiency. Arch dams, for example, are designed to transfer the force of the water to the canyon walls, allowing them to withstand tremendous pressure. In addition, hydroelectric power plays a vital role in managing water resources. Dams can help control floods, provide irrigation for agriculture, and ensure a reliable water supply for communities. By sharing these fun facts, you can pique students' interest and encourage them to explore the world of hydroelectric power further. Make learning exciting by combining facts with visual elements and real-world examples.
How to Explain Hydroelectric Power
Explaining hydroelectric power effectively requires a strategic approach, tailored to your audience's level of understanding. Start with the basic concept: water flowing downhill spins a turbine, which generates electricity. Use simple analogies. For younger students, compare it to a water wheel turning a mill. For older students, relate it to the energy conversion principles they've learned in physics. Visual aids are crucial. Use diagrams, illustrations, or videos to show the components of a hydroelectric power plant (dam, reservoir, penstock, turbine, generator) and how they work together. Break down the process into steps. Explain how water is stored in the reservoir, how it flows through the penstock to the turbine, how the turbine spins the generator, and how the generator produces electricity. Avoid technical jargon. Use clear, simple language that everyone can understand. Relate the topic to real-world examples. Discuss the hydroelectric power plants in your region or country, and explain how they provide electricity to homes and businesses. Encourage questions and discussion. Create a safe and supportive environment where students feel comfortable asking questions and sharing their ideas. Address common misconceptions. Many people mistakenly believe that hydroelectric power is entirely "clean" and has no environmental impacts. Be sure to discuss the potential environmental consequences of dams, such as impacts on fish populations and river ecosystems. Finally, emphasize the importance of responsible and sustainable hydropower development.
What if Hydroelectric Power Disappeared?
Imagine a world without hydroelectric power. The consequences would be far-reaching and affect many aspects of our lives. For starters, electricity prices would likely rise significantly. Hydroelectric power is often a relatively low-cost source of electricity, and its absence would force us to rely more heavily on more expensive sources, such as fossil fuels. This would not only increase energy costs for consumers but also have broader economic impacts, affecting industries that rely on affordable electricity. Furthermore, our carbon footprint would likely increase. Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that produces little to no greenhouse gas emissions. Without it, we would need to burn more fossil fuels to meet our energy needs, contributing to climate change. The reliability of our electricity grid would also be compromised. Hydroelectric plants provide a stable and dispatchable source of power, meaning they can quickly adjust their output to meet changes in demand. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining grid stability and preventing blackouts. Without hydroelectric power, the grid would be more vulnerable to fluctuations in supply and demand. Finally, water management would become more challenging. Dams play a vital role in controlling floods, providing irrigation for agriculture, and ensuring a reliable water supply for communities. Without dams, we would be more susceptible to droughts and floods. While a complete disappearance of hydroelectric power is unlikely, this thought experiment highlights its importance in our energy mix and our economy.
Listicle: 5 Key Things to Know About Hydroelectric Power
Here's a quick rundown of the five most important things to understand about hydroelectric power:
- It's renewable: Hydroelectric power uses the energy of moving water, a resource that is constantly replenished by the water cycle.
- It's relatively clean: Compared to fossil fuels, hydroelectric power produces very little air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions (although reservoirs can release some methane).
- Dams are key: Most hydroelectric plants rely on dams to create reservoirs and control the flow of water to the turbines.
- Environmental impacts exist: Dams can disrupt river ecosystems, affecting fish populations, water quality, and sediment transport.
- It's flexible: Hydroelectric plants can quickly adjust their output to meet changes in electricity demand, making them valuable for grid stability.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about hydroelectric power:
Q: Is hydroelectric power truly renewable?
A: Yes, hydroelectric power is considered a renewable energy source because it relies on the continuous water cycle. As long as rain and snow replenish rivers and streams, hydroelectric power can be generated sustainably.
Q: What are the main environmental concerns associated with hydroelectric power?
A: The primary environmental concerns include the disruption of river ecosystems, the impact on fish populations (especially migratory species), changes in water quality, and potential greenhouse gas emissions from reservoirs.
Q: How efficient is hydroelectric power compared to other energy sources?
A: Hydroelectric power is generally quite efficient, with modern plants often achieving efficiencies of 80% or higher. This means that a large percentage of the water's potential energy is converted into electricity.
Q: What is pumped storage hydroelectricity, and how does it work?
A: Pumped storage hydroelectricity is a type of hydropower that stores energy by pumping water from a lower reservoir to an upper reservoir during periods of low electricity demand. When demand is high, the water is released from the upper reservoir to generate electricity, similar to a conventional hydroelectric plant.
Conclusion of Hydroelectric Power Description for Students and Teachers
Hydroelectric power represents a powerful intersection of natural resources and human ingenuity. By understanding its fundamental principles, historical context, and potential impacts, both students and teachers can engage in meaningful discussions about its role in a sustainable energy future. From exploring the mechanics of turbines and generators to critically examining the environmental considerations surrounding dam construction, there are ample opportunities for exploration, discovery, and informed decision-making. By embracing a holistic approach, we can unlock the full potential of hydroelectric power while minimizing its environmental footprint, ensuring a brighter and more sustainable future for all. Hydroelectric power will continue to be an essential source of energy.