The rush of a waterfall, the quiet hum of a dam – hydroelectric power seems like a clean, sustainable way to light our homes and power our lives. But is it truly a renewable resource, or are there hidden complexities beneath the surface? Let's dive into the facts and myths surrounding hydroelectric power and uncover the truth about its renewable status.
Many of us are grappling with the desire to live more sustainably and reduce our carbon footprint. We're bombarded with information about renewable energy, but it can be challenging to sort through the nuances and understand the complete picture. Is that "green" energy source really as environmentally friendly as it seems? Are we overlooking potential downsides in our quest for clean power?
Yes, hydroelectric power is generally considered a renewable energy source. It harnesses the continuous water cycle – evaporation, precipitation, and flow – to generate electricity. As long as the water cycle continues, we can rely on hydropower. However, it's not without its caveats. The environmental impact of large-scale dams, including habitat disruption and altered river ecosystems, raises important questions about its overall sustainability.
This article will explore the facts and myths surrounding hydroelectric power, examining its benefits and drawbacks. We'll delve into the environmental impacts, the role of reservoirs, and the future of hydropower in a world increasingly focused on renewable energy. Understanding the complexities of hydroelectric power is crucial to making informed decisions about our energy future.
Is Hydroelectric Power Truly Renewable?
The question of whether hydroelectric power is truly renewable often sparks debate. From a purely technical standpoint, it seems straightforward. Rainfall replenishes rivers, and that flowing water spins turbines to create electricity. The water isn't "used up" in the process, and the cycle continues. But the real world is rarely that simple.
I remember visiting the Hoover Dam as a child. The sheer scale of it was awe-inspiring. I understood that it was generating power, but I didn't grasp the ecological changes it had wrought on the Colorado River. It wasn't until years later, studying environmental science, that I began to understand the trade-offs involved.
The construction of large dams can have significant environmental consequences. Reservoirs flood vast areas of land, displacing wildlife and altering natural habitats. The dam itself disrupts the natural flow of the river, affecting fish migration and sediment transport. Downstream ecosystems can suffer from reduced water flow and altered water temperatures. Methane emissions from reservoirs, particularly in tropical regions, are another concern, as methane is a potent greenhouse gas.
While the energy source – flowing water – is renewable, the infrastructure required to harness it can have lasting environmental impacts. Sustainable hydropower development aims to minimize these impacts through careful site selection, fish passages, and other mitigation measures. It's a constant balancing act between energy needs and environmental preservation. The question is not so muchifhydropower is renewable, buthow sustainablywe can harness its power.
The Environmental Impact of Hydroelectric Dams
The environmental impact of hydroelectric dams is a multifaceted issue that requires careful consideration. While hydropower offers the benefit of clean electricity generation, the construction and operation of dams can have significant ecological consequences. These impacts extend beyond the immediate vicinity of the dam and can affect entire river systems.
One of the most significant impacts is the alteration of river ecosystems. Dams disrupt the natural flow of water, leading to changes in water temperature, nutrient levels, and sediment transport. These changes can negatively affect aquatic life, including fish populations, insects, and plants. Fish migration is particularly affected, as dams can block access to spawning grounds.
Reservoirs created by dams flood vast areas of land, displacing wildlife and altering terrestrial habitats. The decomposition of organic matter in reservoirs can also lead to the release of greenhouse gases, such as methane, contributing to climate change. The construction of dams can also lead to soil erosion and sedimentation, further impacting water quality.
However, it's important to note that not all hydropower dams have the same environmental impact. Small-scale hydropower projects, particularly those that divert water without creating large reservoirs, can have a much smaller environmental footprint. Careful planning and mitigation measures can also help to minimize the negative impacts of larger dams. These include fish passages, sediment management strategies, and the restoration of riparian habitats.
Hydroelectric Power: History and Myths
The history of hydroelectric power is surprisingly long, dating back to ancient water wheels used for grinding grain. The modern era of hydropower began in the late 19th century with the development of electric generators. The first hydroelectric power plant was built in 1882 in Appleton, Wisconsin, marking the beginning of a new era in energy production.
One common myth surrounding hydroelectric power is that it's a completely clean and environmentally friendly energy source. While hydropower does not produce greenhouse gas emissions during operation, the construction of dams can have significant environmental impacts, as discussed earlier. It's important to acknowledge these impacts and strive for more sustainable hydropower development.
Another myth is that all hydroelectric dams are large-scale projects that require the flooding of vast areas of land. While large dams do have significant environmental impacts, there are also smaller-scale hydropower projects that can be developed with a smaller environmental footprint. These projects often utilize existing infrastructure, such as canals and irrigation systems, to generate electricity.
The history of hydropower is intertwined with both progress and environmental degradation. Understanding this history and dispelling common myths is crucial for making informed decisions about the future of hydropower. By embracing sustainable practices and innovative technologies, we can harness the power of water while minimizing its environmental impact.
The Hidden Secrets of Sustainable Hydropower
The idea of "sustainable hydropower" may sound like an oxymoron to some, given the well-documented environmental impacts of large dams. However, there's a growing movement towards developing hydropower in a more environmentally responsible way. The "hidden secrets" lie in a combination of innovative technologies, careful planning, and a holistic approach to river management.
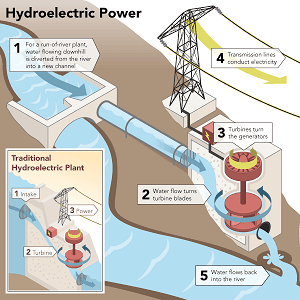
One secret is the increasing use of run-of-river hydropower. These projects divert a portion of the river's flow through a turbine, generating electricity without creating a large reservoir. This minimizes the impact on the river's ecosystem and reduces the risk of flooding. Another secret is the development of fish passages that allow fish to migrate around dams, preserving their natural life cycle.
Furthermore, advanced technologies are being developed to improve the efficiency of hydropower turbines and reduce their environmental impact. These include turbines that are designed to be more fish-friendly and turbines that can operate at lower water flows. Careful planning is also essential. This includes conducting thorough environmental impact assessments, selecting appropriate sites for hydropower projects, and implementing mitigation measures to minimize the negative impacts.
The final "secret" is a holistic approach to river management that considers the entire river basin. This involves balancing the needs of hydropower generation with the needs of other stakeholders, such as agriculture, fisheries, and recreation. By embracing these secrets, we can harness the power of water in a more sustainable way.
Recommendations for Responsible Hydropower Use
So, what can we do to ensure that hydropower is used responsibly? It starts with demanding transparency and accountability from energy companies and governments. We need to push for rigorous environmental impact assessments before new hydropower projects are approved, and we need to hold them accountable for mitigating the negative impacts.
Supporting research and development of more sustainable hydropower technologies is also crucial. This includes investing in run-of-river projects, fish-friendly turbines, and other innovative solutions. Furthermore, we need to promote energy efficiency and conservation to reduce our overall demand for electricity, lessening the need for new hydropower projects.
As consumers, we can choose to support energy providers that prioritize renewable energy sources, including sustainably developed hydropower. We can also advocate for policies that promote renewable energy and protect our rivers and ecosystems. Ultimately, responsible hydropower use requires a collective effort from individuals, businesses, and governments.
We need to recognize that hydropower is not a silver bullet for our energy needs. It's just one piece of the puzzle. A diversified energy portfolio that includes solar, wind, and other renewable sources is essential for a sustainable energy future.
The Role of Reservoirs in Hydropower and Beyond
Reservoirs are an integral part of many hydroelectric power systems, serving as the "water battery" that allows for the storage and release of water as needed to generate electricity. However, their role extends far beyond power generation. They can also provide water for irrigation, drinking water supplies, flood control, and recreational opportunities.
Despite these benefits, reservoirs also have significant environmental impacts. As previously discussed, they can flood vast areas of land, displace wildlife, and alter river ecosystems. The decomposition of organic matter in reservoirs can lead to the release of greenhouse gases, and the altered water flow can affect downstream water quality and fish populations.
Managing reservoirs in a sustainable way is crucial for minimizing their negative impacts and maximizing their benefits. This includes optimizing water release schedules to balance the needs of power generation with the needs of other stakeholders, such as agriculture and fisheries. It also involves implementing measures to control the release of greenhouse gases and improve water quality.
In some cases, decommissioning dams and restoring rivers may be the best option for achieving environmental sustainability. This is a complex process that requires careful planning and consideration of the potential economic and social impacts. However, it can lead to significant ecological benefits, including the restoration of fish populations and the improvement of water quality.
Tips for Evaluating the Sustainability of Hydropower Projects
Evaluating the sustainability of hydropower projects can be challenging, as there are many factors to consider. However, there are several key questions you can ask to assess the environmental and social impacts of a project.
First, consider the location of the project. Is it located in a sensitive ecosystem or near a protected area? Will it displace local communities or disrupt their traditional way of life? Second, assess the size of the reservoir. How much land will be flooded, and what are the potential impacts on wildlife and habitats?
Third, examine the design of the dam and turbines. Are they designed to minimize the impact on fish populations and water quality? Are there fish passages to allow fish to migrate around the dam? Fourth, investigate the management of the reservoir. Are water release schedules optimized to balance the needs of power generation with the needs of other stakeholders?
Finally, look for independent certifications that verify the sustainability of the project. The Hydropower Sustainability Assessment Protocol (HSAP) is one such certification that assesses the environmental, social, and economic impacts of hydropower projects. By asking these questions and seeking out independent certifications, you can make informed decisions about the sustainability of hydropower projects.
The Future of Hydropower: Innovation and Sustainability
The future of hydropower lies in innovation and sustainability. As the world transitions to a low-carbon economy, hydropower will continue to play an important role in providing clean electricity. However, it's crucial that hydropower development is done in a way that minimizes environmental impacts and maximizes social benefits.
One promising area of innovation is the development of closed-loop hydropower systems. These systems utilize pumped storage to store water and generate electricity on demand. They can be located off-stream, reducing the impact on river ecosystems. Another area of innovation is the development of small-scale hydropower projects that utilize existing infrastructure, such as canals and irrigation systems.
Furthermore, advances in materials science and engineering are leading to the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly turbines. These turbines are designed to minimize the impact on fish populations and operate at lower water flows. Sustainability will also depend on more holistic planning that addresses the long-term environmental consequences in the design of hydroelectric plants.
The future of hydropower will depend on a commitment to innovation, sustainability, and responsible development. By embracing these principles, we can harness the power of water while minimizing its environmental impact and maximizing its social benefits.
Fun Facts About Hydroelectric Power
Hydropower is not only a significant source of electricity but also boasts some fascinating facts. Did you know that the world's largest hydroelectric power plant is the Three Gorges Dam in China? It has a generating capacity of over 22,500 megawatts, enough to power millions of homes.
Another interesting fact is that Norway is almost entirely powered by hydropower. Over 95% of Norway's electricity comes from hydroelectric sources, making it one of the most renewable energy-dependent countries in the world. Hydropower is one of the oldest forms of energy generation, with water wheels being used for centuries to grind grain and power machinery.
The Hoover Dam, one of the most iconic hydroelectric dams in the United States, was built during the Great Depression and provided jobs for thousands of workers. It created Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States by volume. The Grand Coulee Dam, another major hydroelectric dam in the United States, is so large that it can be seen from space.
These fun facts highlight the significance of hydropower in the history of energy production and its continued importance in providing clean electricity. However, it's important to remember that hydropower is not without its environmental impacts. By embracing sustainable practices and innovative technologies, we can harness the power of water while minimizing its negative consequences.
How to Support Sustainable Hydropower Development
Supporting sustainable hydropower development requires a multifaceted approach that involves advocating for responsible policies, investing in innovative technologies, and making informed consumer choices. As individuals, we can play a role in promoting hydropower projects that minimize environmental impacts and maximize social benefits.
One way to support sustainable hydropower is to advocate for policies that require rigorous environmental impact assessments before new projects are approved. These assessments should consider the potential impacts on fish populations, water quality, and local communities. We can also support policies that promote the development of run-of-river hydropower projects, which have a smaller environmental footprint than large dams.
Another way to support sustainable hydropower is to invest in companies that are developing innovative technologies, such as fish-friendly turbines and closed-loop hydropower systems. These technologies can help to minimize the environmental impacts of hydropower and make it a more sustainable energy source. As consumers, we can choose to purchase electricity from providers that source their power from sustainable hydropower projects.
We can also support organizations that are working to protect rivers and promote sustainable hydropower development. These organizations often conduct research, advocate for responsible policies, and educate the public about the importance of sustainable hydropower. By taking these steps, we can help to ensure that hydropower continues to play a role in providing clean electricity while minimizing its environmental impacts.
What If We Stopped Using Hydropower?
Imagining a world without hydropower raises some interesting questions about our energy future. Hydropower currently provides a significant portion of the world's electricity, so phasing it out completely would have a substantial impact on our energy supply. The immediate consequence would be a need to replace that generating capacity with other sources.
The most likely replacements would be other renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal. However, these sources are intermittent and require energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable supply of electricity. Fossil fuels, such as coal and natural gas, could also be used to replace hydropower, but this would increase greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbate climate change.
The economic impacts of phasing out hydropower would also be significant. Hydropower projects provide jobs and revenue for local communities. Phasing them out would result in job losses and economic disruption. Furthermore, the cost of replacing hydropower with other sources could be substantial, potentially leading to higher electricity prices.
While phasing out hydropower completely may not be feasible or desirable, it's important to consider the potential consequences and explore alternative energy sources that can provide clean and reliable electricity with minimal environmental impacts. A diversified energy portfolio that includes a mix of renewable energy sources is essential for a sustainable energy future.
Listicle: 5 Key Facts About Hydroelectric Power
Let's break down the core information about hydroelectric power into a concise list:
- Renewable Resource: Hydropower is considered renewable because it relies on the continuous water cycle.
- Environmental Impact: Dams can disrupt river ecosystems, alter habitats, and impact fish populations.
- Sustainability Efforts: Run-of-river projects and fish passages are designed to minimize environmental damage.
- Global Significance: Hydropower is a major source of electricity worldwide, especially in countries like Norway and China.
- Future Innovations: Closed-loop systems and advanced turbine designs are aimed at enhancing sustainability.
These facts provide a snapshot of the key aspects of hydroelectric power, from its renewable nature to its environmental challenges and the ongoing efforts to improve its sustainability.
Question and Answer
Here are some frequently asked questions about hydroelectric power:
Q: Is hydroelectric power a completely clean energy source?
A: No, while hydropower doesn't produce greenhouse gases during operation, the construction of dams can have significant environmental impacts.
Q: What are the main environmental concerns associated with hydroelectric dams?
A: The main concerns include disruption of river ecosystems, alteration of habitats, and impacts on fish populations.
Q: What is run-of-river hydropower?
A: Run-of-river hydropower diverts a portion of the river's flow through a turbine, generating electricity without creating a large reservoir, thus minimizing environmental impact.
Q: What can be done to make hydropower more sustainable?
A: Sustainable practices include careful site selection, fish passages, run-of-river projects, and advanced turbine designs.
Conclusion of Is Hydroelectric Power a Renewable Resource? Facts vs. Myths
Hydroelectric power presents a complex picture in the world of renewable energy. While it harnesses a naturally replenishing resource – water – the infrastructure required to capture that power can have significant ecological consequences. The key takeaway is that not all hydropower is created equal. Sustainable practices, innovative technologies, and responsible planning are crucial to minimizing the environmental impact and maximizing the benefits of this energy source. As we move toward a cleaner energy future, a balanced and informed approach to hydropower is essential.